Enhancing endpoint monitoring with threat intelligence
When investigating endpoints, SOC analysts need as much telemetry as possible because there are often many attack vectors in play. For example, a malicious PowerShell script can invoke various commands to install software such as ransomware. To give analysts as much information as possible to enrich incidents, it's highly recommended that you incorporate threat intelligence.
This article assumes the reader has Splunk Mission Control and Splunk Threat Intelligence Management enabled.
Required data
Intelligence workflows
Using cloud services such as Splunk Mission Control or Splunk Enterprise Security provides the most flexibility for configuring many threat intelligence sources such as Splunk Threat Intelligence Management and other third-party vendors like Recorded Future, Crowdstrike, etc. After the feeds are active, incidents automatically receive added threat intelligence. If a match occurs, the analyst gains additional insights from the incident. For example, the hdoor.exe observable shown in the image below reflects a high threat intelligence score.
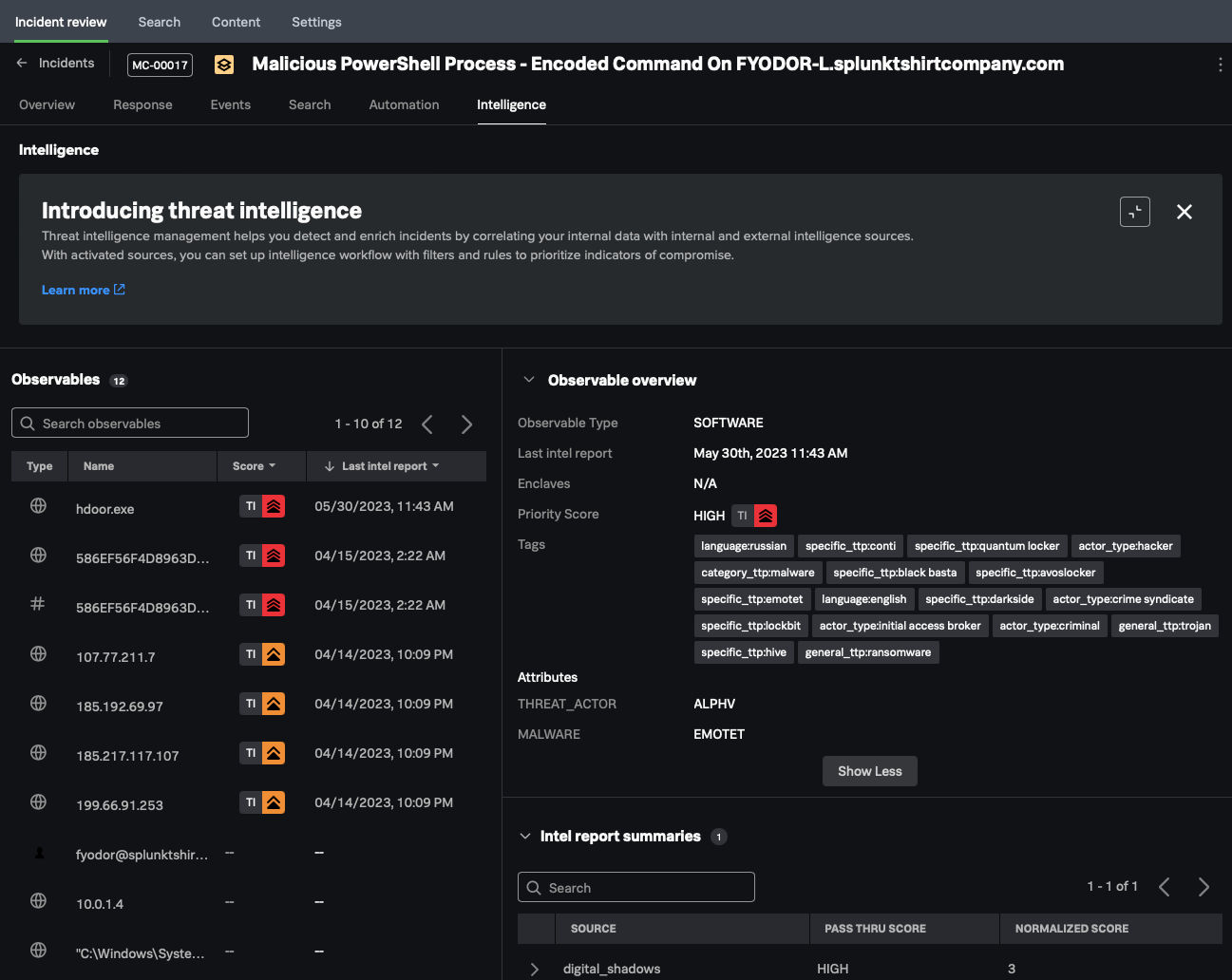
The intelligence management framework saves an analyst time with the notable event auto-submission process. Analysts retain full control over the process with manual override features. You can auto-enrich events using Splunk Enterprise Security.
Gathering threat feeds for Splunk Mission Control and Splunk Enterprise Security
The information in this article applies to Splunk Enterprise Security (ES) versions 7.x. If you have upgraded to Splunk Enterprise Security version 8.x, some terminology and steps might not apply. For additional assistance on this use case with ES 8.x, Splunk Professional Services can help.
Splunk Threat Intelligence Management is available to Splunk Mission Control and Splunk Enterprise Security for cloud stacks. However, before gaining access to its vast threat intelligence network, you need to configure it for the appropriate stacks. Modular input definitions in inputs.conf for Splunk Mission Control must be considered and consist of the following:
- Read IM subscription status
- Retrieve IM indicators
- Parse IM indicator files
- Splunk Enterprise Security TIF intelligence downloads to add threat intelligence automatically as threatlists
In addition to inputs, you need to consider KV store collection definitions, which are defined in collections.conf and transforms.conf. Workflow actions (defined in workflow_actions.conf) assist with navigation from Splunk Enterprise Security risk notable events to Splunk Mission Control. Finally, telemetry retrieve and parse IM indicators report on conditions such as enabling and disabling. The retrieved and parsed results are not logged.
Splunk Enterprise Security interoperability
When triaging notable events in Splunk Enterprise Security, threat feeds provide context and enrichment for matching events. An adaptive response action link in the notable event launches the corresponding incident in Splunk Mission Control. To access links to Splunk Mission Control from Splunk Enterprise Security follow these steps:
- Go to Incident Review and expand the notable event of interest. In the lower right of the notable event information is the Adaptive Responses section.
- Click any of the links that begin with TruSTAR.
TruSTAR is now Splunk Threat Intelligence Management.
The analyst now has the ability to gain additional insights from the event data in Splunk Mission Control.
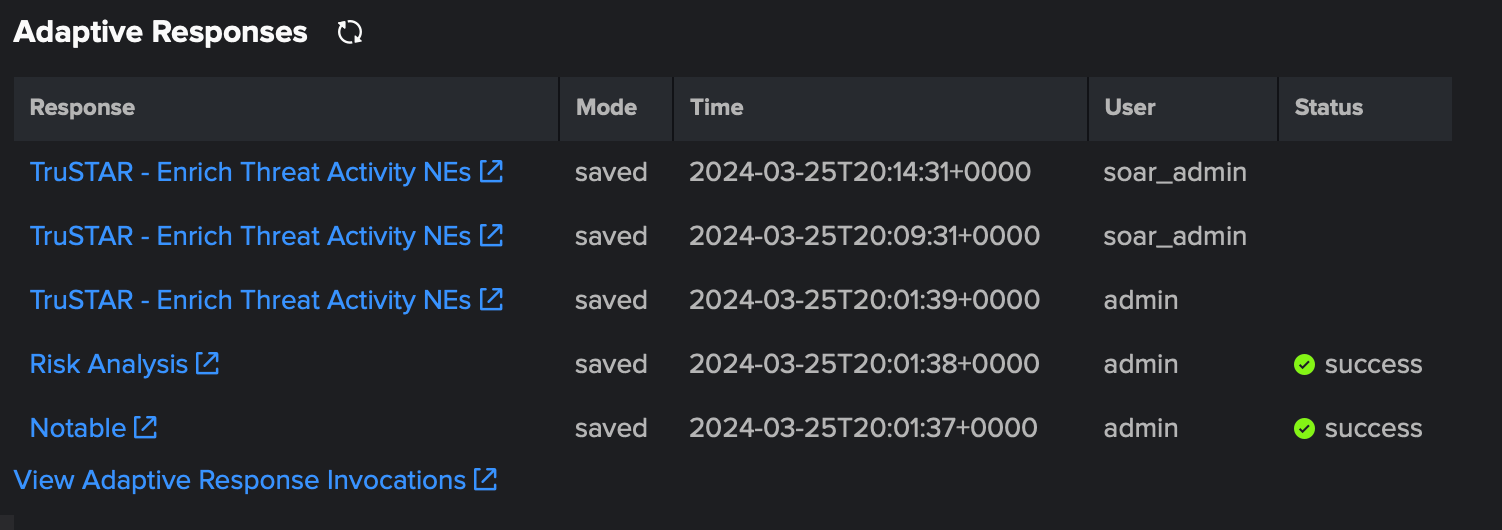
Next steps
These resources might help you understand and implement this guidance:
- Splunk Docs: Available premium intelligence sources for Splunk Mission Control
- Splunk Docs: Access Threat Intelligence Management in Splunk Mission Control
- Getting Started Guide: Getting started - Splunk Intel Management (TruSTAR)

