Choosing KPI base searches over ad hoc searches
Some of your KPIs display N/A instead of a value on your dashboards in Splunk ITSI. You need to resolve this so you can get KPI and Health Score values.
This article is part of the Definitive Guide to Best Practices for IT Service Intelligence. ITSI administrators will benefit from adopting this practice as they work on Service Insights.
Solution
Multiple KPIs can be powered by the same dataset to dramatically reduce search load and reduce unknown KPI values. Using base searches results in one search for multiple KPIs, which means you run fewer searches and use less time, so there is more capacity for additional searches. If you don't use base searches, each KPI runs on its own schedule and uses up more capacity.
For example, you might be able to create a base search that powers four KPIs and runs 129 times per day. If you had an ad hoc search for each of those KPIs, that would mean 516 searches running each day. Search capacity is limited by the number of search slots that are available. If a KPI search cannot execute due to search capacity constraints, it displays N/A for an unknown value. This unknown value interferes with service Health Score calculation, which then leads to potentially unreliable actions. The base search reduces searches being run by 75 percent.

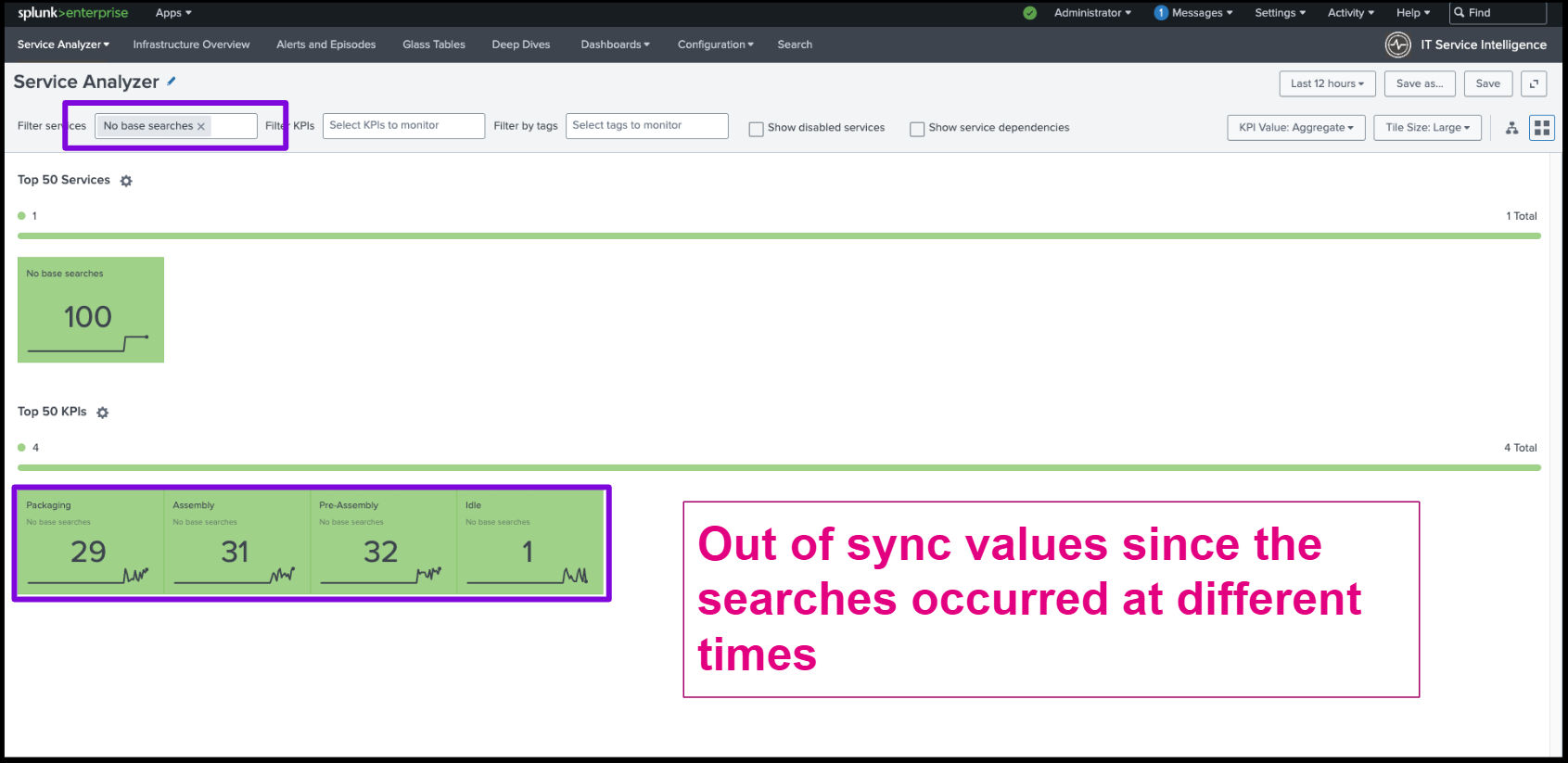
In addition, base searches help KPIs stay in sync. When KPIs run at different times, you get out-of-sync values, which can also lead to unreliable health scores. In this example, ad hoc searches run at different times give an incomplete picture. The health score of the service is 100, but we only see a total value of 93 when looking at the KPIs.
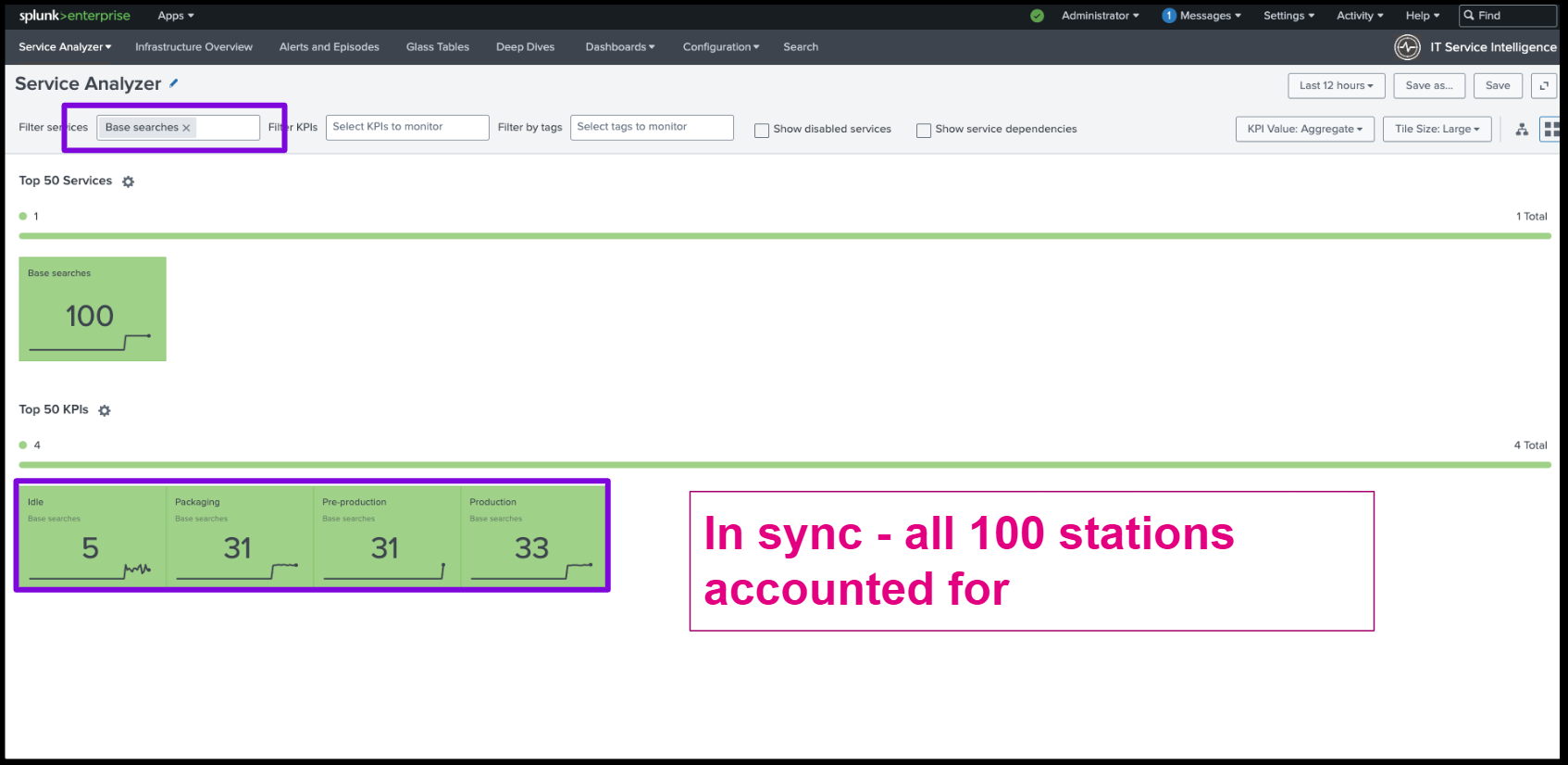
In this second example, when base searches have been applied, all 100 stations are accounted for.
Next steps
You might also be interested in the following Splunk resources:
- Splunk Docs: Service insights manual
- Splunk Blog: Top 3 best practices for configuring Splunk ITSI in a large-scale environment

